Looking to expand your knowledge of powerful medicines? Explore the fascinating world of antibiotics that start with the letter “P.” From penicillin to peptidoglycan inhibitors, these drugs play a crucial role in fighting bacterial infections. Dive in to discover some of the most important antibiotics beginning with “P” and how they help keep us healthy!
1. Penicillin G
Penicillin G, also known as Benzylpenicillin, is a type of penicillin antibiotic that effectively fights many bacterial infections. It works by killing bacteria or stopping their growth, making it a powerful antimicrobial.
Health Benefits: It is used to treat infections like pneumonia, strep throat, and syphilis. It is strong against many bacteria causing common infections.
How to Take It: Usually given by injection in hospitals. Dose depends on the infection but commonly ranges from 1-4 million units per day.
Compatibility: Used for bacterial infections, especially respiratory and skin infections. Works well with an empty stomach and may be combined with other antibiotics if needed.
2. Penicillin V
Penicillin V, or Phenoxymethylpenicillin, is an oral antibiotic that fights bacteria. It is similar to Penicillin G but can be taken by mouth, making it easier to use outside hospital settings.
Health Benefits: Effective for throat infections, ear infections, and skin infections caused by bacteria.
How to Take It: Usually taken as tablets or liquids, typically 250 mg to 500 mg every 6-8 hours.
Compatibility: Suitable for mild bacterial infections, best taken on an empty stomach. Pair with probiotics for gut health if long-term use is needed.
3. Piperacillin
Piperacillin is an antibiotic that targets a wide range of bacteria, especially those causing pneumonia and bloodstream infections. It is often used in hospitals for serious infections.
Health Benefits: Good at fighting bacteria like Pseudomonas aeruginosa, especially in complicated infections.
How to Take It: Usually given by injection or infusion in hospitals; dose varies based on severity.
Compatibility: Used in severe bacterial infections, often with other antibiotics like tazobactam. It’s not suitable for viral infections.
4. Piperacillin/tazobactam
This is a combined antibiotic product that includes Piperacillin and Tazobactam. It enhances the ability to fight bacteria and is commonly used in hospital treatments.
Health Benefits: Treats respiratory, urinary, and skin infections resistant to other antibiotics.
How to Take It: Administered via IV, typically in hospitals, with doses adjusted for infection severity.
Compatibility: Used for serious infections; works well with resistant bacteria. Not suitable for viral illnesses.
5. Polymyxin B
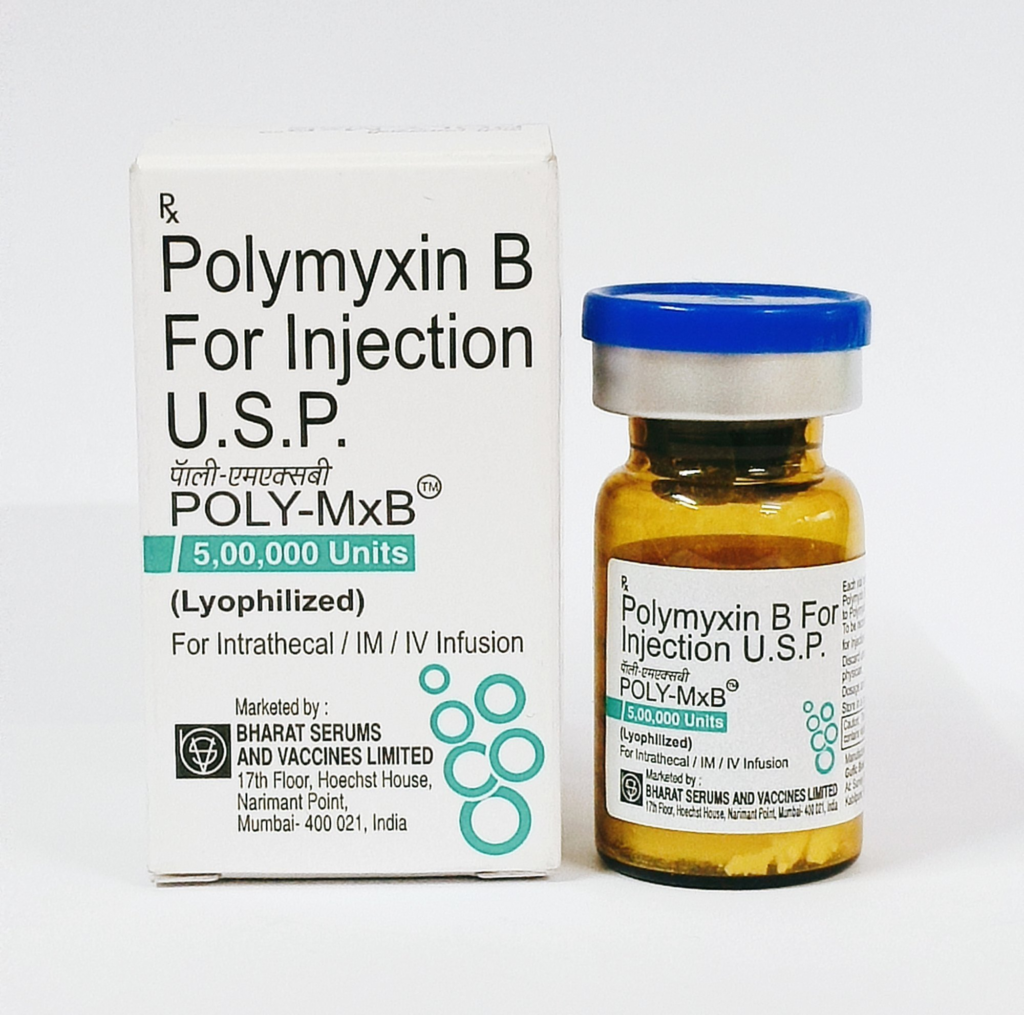
Polymyxin B is a polypeptide antibiotic mainly used for resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. It disrupts bacterial cell membranes.
Health Benefits: Effective against multidrug-resistant bacteria like Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter.
How to Take It: Usually given by injection in hospital settings; dose depends on infection severity.
Compatibility: Reserved for resistant infections; potential kidney toxicity requires careful monitoring.
6. Colistin (Polymyxin E)
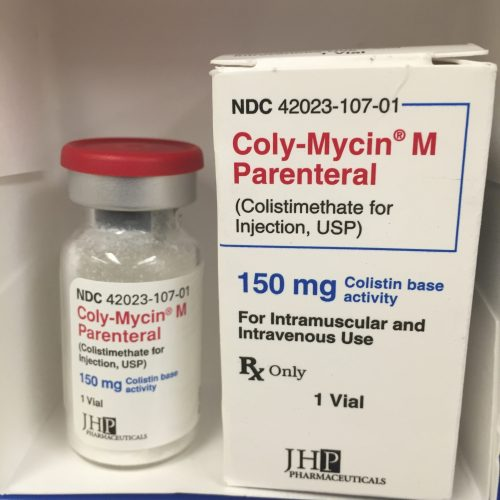
Colistin, or Polymyxin E, is similar to Polymyxin B and used against resistant Gram-negative bacteria. It is often used when other antibiotics fail.
Health Benefits: Critical for fighting multidrug-resistant infections, especially in hospitals.
How to Take It: Administered intravenously; dosage varies based on patient condition.
Compatibility: Used in serious infections like pneumonia in ventilated patients. Needs to be used cautiously due to potential kidney damage.
7. Penicillin/Streptomycin Solution
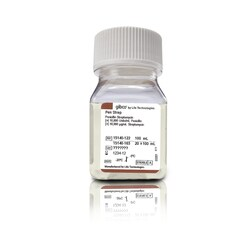
This is a laboratory antibiotic mixture used mainly in research and cell culture to prevent bacterial contamination.
Health Benefits: Not used directly for medical treatment; important in scientific research.
How to Take It: Applied in laboratory settings, not for ingestion or external use.
Compatibility: Used with cell cultures and lab procedures; not suitable for human use.

Eleena Wills is a passionate health and wellness writer with over 5 years of experience in simplifying complex health topics for everyday readers. She holds a background in health communication and has contributed to multiple reputable wellness platforms. Eleena is committed to sharing science-backed tips on nutrition, mental well-being, fitness, and lifestyle habits that support long-term health. When she’s not writing, she’s experimenting with healthy recipes or practicing yoga.
