Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of teeth.
It is caused by bacteria that grow in the dental plaque and can lead to inflammation and destruction of the gum tissue and bone that surround and support the teeth.
There are different stages of periodontal disease, and each stage requires different treatments to prevent further damage and preserve the health of the teeth and gums.
In this article, we will discuss the five stages of periodontal disease, the new classification of periodontal disease, and how to recognize each stage.
What is Periodontal Disease?
Before discussing the stages of periodontal disease, it’s important to understand what periodontal disease is and how it affects the teeth and gums.
Periodontal disease is a bacterial infection that affects the gums and supporting structures of teeth. It is caused by the accumulation of dental plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and gums.
When the dental plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar or calculus, which cannot be removed by brushing alone.
Tartar buildup can lead to the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums, where bacteria can thrive and cause inflammation and infection.
The earliest stage of periodontal disease is gingivitis, which is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums.
Gingivitis is reversible with proper oral hygiene and professional dental cleaning. If left untreated, however, gingivitis can progress to more severe stages of periodontal disease.
Stages of Periodontal Disease With Pictures
Let’s take a look at the stages of periodontal disease with pictures before getting a proper explanation about them.
Stage 1- Gingivitis
Stage 2. Early Periodontal
Stage 3- Moderate Periodontal
Stage 4- Advanced Periodontal
How Many Stages of Periodontal Disease are There?
Let’s talk about what are the 5 stages of periodontal disease.
Stage 1: Gingivitis
The earliest stage of periodontal disease is gingivitis. At this stage, the gums are inflamed due to the buildup of plaque and bacteria along the gum line.
Its symptoms include red, swollen, or bleeding gums. However, at this stage, there is no permanent damage to the bone or other tissues that support the teeth.
Gingivitis can often be reversed with improved oral hygiene habits and regular dental cleanings.
Stage 2: Early Periodontitis
If gingivitis is left untreated, the patient can get early periodontitis. At this stage, the infection begins to affect the bone and connective tissue that hold the teeth in place.
You may experience some bone loss and deeper pockets between your teeth and gums. Regular dental cleanings and improved oral hygiene can still help prevent further damage and reverse some of the early symptoms.
Stage 3: Moderate Periodontitis
In moderate periodontitis, the damage to the bone and connective tissue becomes more significant, and the pockets between the teeth and gums deepen further.
Tooth mobility may also become noticeable. Treatment may include more aggressive cleaning procedures, such as scaling and root planing, as well as other treatments like gum surgery or bone grafting.
Stage 4: Advanced Periodontitis
Periodontal Disease is the most advanced stage of gum disease, and it’s characterized by significant damage to the gums, bone, and other tissues that support your teeth.
At this stage, your teeth may feel loose, and you may even experience tooth loss if the disease isn’t treated.
The primary cause of the advanced periodontal disease is the buildup of plaque and bacteria on your teeth and gums. This leads to inflammation and infection, which can gradually damage the tissues that hold your teeth in place.
Stage 5- Refractory Periodontal
It is when the periodontal isn’t reacting to the treatment.
New Classification of Periodontal Disease
In 2017, the American Academy of Periodontology (AAP) released a new classification system for periodontal disease.
The new system is based on a combination of clinical and radiographic findings and is intended to help dentists and periodontists better diagnose and treat periodontal disease.
Stage 5- Refractory Periodontal
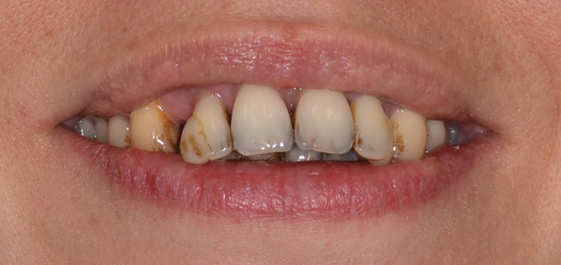
This stage occurs when periodontitis fails to respond to treatment and continues to progress. It may be caused by underlying health conditions or genetic factors, and treatment may involve more advanced techniques like antibiotics, laser therapy, or genetic testing.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is Stage 2 of Periodontal Disease?
This stage is marked by the beginning of bone loss and the formation of periodontal pockets (spaces between the teeth and gums). Treatment may include scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), along with improved oral hygiene practices.
What is Stage 3 of Periodontal Disease?
At this stage, there is further bone loss and the periodontal pockets become deeper. Treatment may involve more extensive scaling and root planing, along with other periodontal procedures like gum grafts or bone regeneration.
What is Stage 5 of Periodontal Disease?
Stage 5 of periodontal disease occurs when this disease isn’t responding to treatment, and is spreading further due to some underlying causes.
Which Condition is the Earliest Stage of Periodontal Disease?
Stage I: Gingivitis is the first stage which is characterized by inflammation of the gums without any loss of bone or tissue

Jean Smith is a fitness enthusiast and blogger who focuses on fitness and a healthy lifestyle. She is passionate about assisting people in living healthier lifestyles and is constantly on the lookout for new and creative methods to stay fit and healthy. Her articles are excellent resources for anyone interested in improving their health and fitness.
