Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a widely discussed yet often misunderstood condition.
It affects individuals across various ages, impacting their daily lives, learning abilities, and social interactions.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify ADHD, offering valuable insights for beginners who seek to understand this condition better.
The journey of understanding ADHD is akin to navigating a complex river system. There are twists and turns, often leading to unexpected destinations.
It’s a path that requires patience, empathy, and an eagerness to learn. As we delve into the intricacies of ADHD, we also touch upon the significance of private PTSD assessments, like those offered by Augmentive, a leading name in mental health support.
Understanding the intersection between ADHD and PTSD is crucial, as both can coexist, influencing one’s mental well-being in profound ways.
ADHD is not just a childhood condition; it spans across the lifetime, affecting adults in unique ways. It’s a spectrum, with symptoms ranging from inattention to hyperactivity and impulsivity.
The key to managing ADHD lies in understanding its facets, adapting to its challenges, and embracing the strengths it can bring.
The ADHD Spectrum: More Than Just Hyperactivity
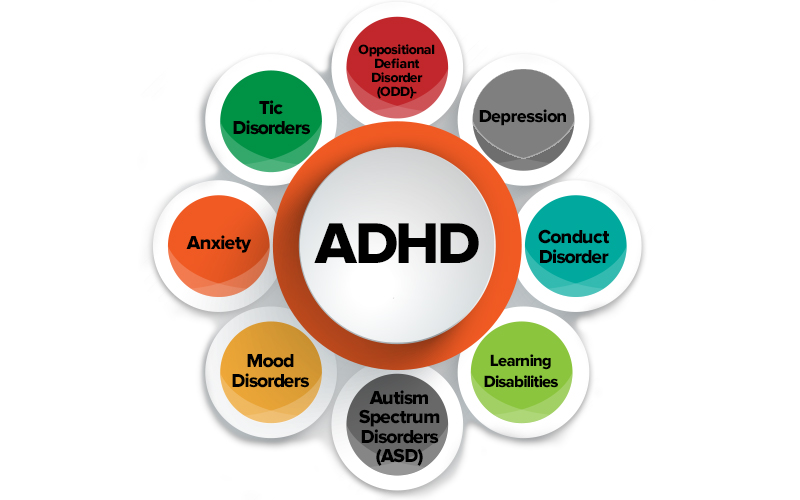
ADHD, often misinterpreted as merely a hyperactive behavior, is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder.
It’s essential to understand that ADHD manifests in three primary subtypes: predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive, and combined.
Each subtype presents a unique set of challenges and symptoms. For instance, the inattentive type may need help with maintaining focus, organizing tasks, or following instructions, often leading to a misconception of laziness or lack of intelligence.
Conversely, the hyperactive-impulsive type is characterized by excessive energy and impulsive actions, which can be misconstrued as disruptive behavior. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective management and empathy towards those with ADHD.
Diagnosis: The First Step to Understanding
A proper diagnosis is the cornerstone of understanding and managing ADHD. It’s a process that requires a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals, often involving a series of interviews, behavioral assessments, and sometimes, neurological testing.
Misdiagnosis or self-diagnosis can lead to inadequate treatment. A professional diagnosis considers various factors, including the individual’s age, the onset of symptoms, and their impact on different aspects of life.
This rigorous approach ensures that the treatment plan is tailored to the individual’s specific needs, improving the effectiveness of interventions.
ADHD in Adults: A Different Shade
Adult ADHD is often overlooked, with many adults unaware that the challenges they face are related to ADHD. Adult ADHD can manifest in various forms, like difficulty in time management, organizational issues, problems in maintaining relationships, or chronic procrastination.
It’s not uncommon for adults with ADHD to have developed coping mechanisms that mask their symptoms, making diagnosis more challenging.
Recognizing ADHD in adulthood is crucial for accessing appropriate treatments and strategies that can significantly improve quality of life.
The Role of Medication in ADHD Management
Medication is a common and effective treatment for ADHD, but it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. Stimulants like methylphenidate and amphetamines are often prescribed, but non-stimulant medications are also available.
Each class of medication works differently and has its own set of potential side effects. It’s important for individuals and their healthcare providers to closely monitor the effects of these medications and adjust dosages or try different medications as needed.
Medication, when combined with other treatments like behavioral therapy, can significantly improve symptoms.
Behavioral Strategies for Coping with ADHD
Behavioral strategies are a vital component of ADHD management, especially when combined with medication. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), time management training, and skills training can be highly effective.
These strategies focus on changing negative thought patterns, improving organizational skills, and teaching effective coping mechanisms.
For children, behavior therapy often involves parents and teachers and might include social skills training. For adults, CBT can help in managing time, setting goals, and maintaining focus on daily tasks.
The Impact of Diet and Exercise
While diet and exercise are not direct treatments for ADHD, they can play a supportive role in overall management.
A balanced diet, including omega-3 fatty acids, and consistent exercise can improve brain function, reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, and improve concentration and energy levels.
It’s important to note, however, that diet and exercise should complement other treatment methods rather than replace them.
Understanding Comorbidities: ADHD and PTSD

ADHD often coexists with other mental health conditions, including PTSD. This comorbidity can complicate diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of PTSD, such as hyperarousal and difficulty concentrating, can mimic or exacerbate ADHD symptoms. Therefore, a comprehensive approach to treatment that addresses both conditions is vital.
Private PTSD assessments, like those offered by Augmentive, can be an integral part of this process, providing specialized evaluation and treatment recommendations.
These assessments are particularly crucial because PTSD symptoms can sometimes overshadow or be mistaken for ADHD, leading to misdiagnosis.
Navigating Social Relationships with ADHD
Individuals with ADHD may face unique challenges in social interactions. Difficulties with impulse control, attention, and hyperactivity can impact their ability to form and maintain relationships.
This part of the guide would offer practical advice on navigating social situations, understanding social cues, and fostering effective communication.
It also emphasizes the importance of building a supportive network and seeking professional help when needed, as social skills can be improved with practice and guidance.
ADHD in the Workplace: Strategies for Success
ADHD can present challenges in the workplace, but with the right strategies, individuals with ADHD can thrive in their professional lives.
This section will provide tips on organization, time management, and how to advocate for reasonable accommodations under employment laws.
It also addresses the importance of finding a career that aligns with the individual’s strengths and interests, which can make managing ADHD symptoms more manageable.
Educational Support for Children with ADHD
For children with ADHD, support in the educational setting is crucial for their academic and social success. This part would explore how parents and educators can collaborate to provide the necessary support.
It would cover topics like Individualized Education Plans (IEPs), classroom accommodations, and teaching strategies tailored to children with ADHD.
The goal is to create an inclusive and supportive learning environment that addresses the specific needs of children with ADHD, helping them to reach their full potential.
In summary, understanding and managing ADHD is a multifaceted process that requires a comprehensive and individualized approach.
From accurate diagnosis to tailored treatment plans, including behavioral strategies, medication, and lifestyle modifications, each aspect plays a vital role in improving the quality of life for those with ADHD.
Additionally, recognizing and addressing comorbid conditions like PTSD is crucial. With the right support and resources, individuals with ADHD can overcome challenges and lead fulfilling lives.

Jean Smith is a fitness enthusiast and blogger who focuses on fitness and a healthy lifestyle. She is passionate about assisting people in living healthier lifestyles and is constantly on the lookout for new and creative methods to stay fit and healthy. Her articles are excellent resources for anyone interested in improving their health and fitness.
