Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has gained immense popularity for its potential in enhancing tissue repair and revitalization.
Whether used in cosmetic treatments or for various orthopedic and dermatological applications, PRP’s effectiveness largely depends on how it’s prepared.
Two primary methods exist: PRP machines and manual preparation techniques. In this discussion, we will delve into the pros and cons of each approach, shedding light on which might be more suitable for specific circumstances.
Precision and Consistency
PRP Machines: Ensuring Precision
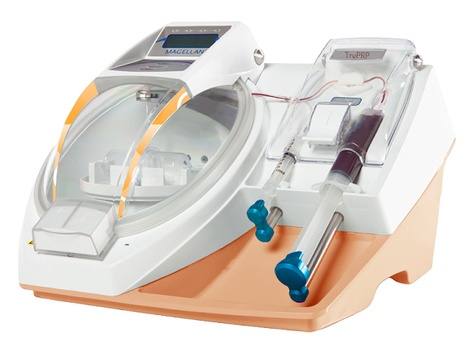
PRP machines are engineered to deliver a level of precision that is challenging to achieve with manual preparation methods.
These machines follow meticulously programmed protocols that ensure the resulting PRP is consistent in terms of platelet concentration and composition.
The SELPHYL® system’s PRP machine employs advanced technology to precisely control the separation of platelets from the patient’s blood sample.
It takes into account factors like centrifugation speed, time, and temperature, resulting in a PRP product with a standardized platelet count.
This consistency is paramount, especially in medical applications, as it ensures that each patient receives the same quality and concentration of therapeutic platelets, enhancing the predictability of outcomes.
Manual Preparation: Variability and Human Factors
Manual PRP preparation relies heavily on the skill and experience of the practitioner. While proficient healthcare professionals can produce good results, there is inherent variability in the process.
Numerous factors, such as the blood collection technique, centrifugation speed, and timing, can all influence the quality and concentration of the final PRP product.
Human factors, such as individual technique and proficiency, can introduce inconsistencies in the process. Even small deviations from the ideal conditions can lead to variations in PRP quality.
This variability can make it challenging to predict treatment outcomes accurately and may require adjustments in the treatment plan for each patient.
Consequently, in scenarios where precision and consistency are paramount, PRP machines often have the advantage.
Speed and Efficiency
PRP Machines: Swift and Streamlined
PRP machines have revolutionized the process of preparing Platelet-Rich Plasma, making it notably swift and highly efficient.
These advanced devices are equipped with pre-set protocols and automated functions that reduce human intervention, ensuring a consistent and speedy outcome.
One significant advantage of PRP machines is their ability to process blood samples rapidly. These machines can spin blood in high-speed centrifuges, separating the platelets and plasma from other blood components in a matter of minutes.
This efficiency is particularly valuable in medical environments where time is often a critical factor. Patients can experience shorter wait times, and healthcare providers can accommodate more patients throughout the day.
Moreover, the streamlined nature of PRP machines reduces the likelihood of human error. Manual PRP preparation involves multiple manual steps that require precise timing and technique.
PRP machines eliminate much of this variability, resulting in a more dependable and reproducible PRP product.
Manual Preparation: Time-Consuming
In contrast, manual PRP preparation can be a time-consuming process, often requiring more steps and human involvement. Each step, from blood collection to the actual PRP separation, demands careful attention to detail and timing.
Blood collection itself can be a relatively straightforward procedure when performed by a skilled phlebotomist. However, the subsequent steps can be quite time-intensive.
After collecting the blood, it needs to be processed through centrifugation, which may take a longer time compared to PRP machines.
During centrifugation, the operator must carefully monitor the process to ensure the separation of the platelet-rich layer from other components.
The time consumed during manual preparation can result in extended waiting times for patients, potentially leading to decreased patient satisfaction, especially in settings where efficiency is highly valued.
Furthermore, the reliance on manual techniques introduces an element of variability that may not be ideal in applications requiring precise and consistent PRP quality.
Contamination Risk
PRP Machines: Reduced Contamination Risk
PRP machines are designed with a primary focus on maintaining a sterile environment throughout the PRP preparation process.
These devices typically employ closed systems that drastically reduce the risk of contamination. From the moment the blood sample is collected to the final separation of platelet-rich plasma, the entire procedure takes place within a sealed and controlled environment.
This closed-system approach ensures that external contaminants, such as airborne particles or microbes, are kept at bay.
As a result, the PRP generated by these machines tends to be more consistent and pure. This is especially vital in medical applications where patient safety and treatment efficacy are paramount.
The reduced risk of contamination provides healthcare providers and patients alike with confidence in the quality of the PRP product.
Manual Preparation: Potential Contamination
Manual PRP preparation, while effective when performed by skilled practitioners in a sterile setting, inherently carries a higher potential for contamination.
This method involves multiple steps, including the collection of blood, centrifugation, and the transfer of PRP into treatment vials. Each transfer introduces an opportunity for contaminants to enter the PRP product.
Even with rigorous adherence to sterilization protocols, human error and unforeseen variables can sometimes compromise the sterility of the process.
Factors such as air exposure, inadequate cleaning, or suboptimal handling can introduce contaminants that may not be immediately evident but could affect the quality of the PRP.
Consequently, in situations where contamination is a critical concern, as in certain medical procedures, the use of PRP machines with their closed systems is often preferred to minimize this risk.
Cost Considerations

PRP Machines: Initial Investment
When considering the cost of incorporating PRP into medical or aesthetic procedures, the initial investment in PRP machines should be a central point of focus.
High-quality PRP machines, often come with a substantial price tag. These machines are engineered to provide precision, consistency, and reduced contamination risk, making them a valuable asset in healthcare settings.
While the upfront cost may appear daunting, it’s essential to view it as a long-term investment. PRP machines can streamline the preparation process, significantly reducing the time and effort required to generate PRP.
This efficiency translates into cost savings over time by reducing the need for extensive manual labor and minimizing the variability in PRP quality.
Moreover, PRP machines are designed to be durable and reliable, requiring minimal maintenance. This means that, once purchased, they can serve a clinic or practice for many years, providing a consistent supply of high-quality PRP.
Manual Preparation: Lower Initial Costs
In contrast to PRP machines, manual PRP preparation typically involves lower initial costs. It doesn’t require the purchase of expensive machinery. However, it’s important to consider the long-term financial implications.
Manual preparation methods may be less costly upfront, but they can lead to higher operational expenses over time.
Achieving consistent PRP quality with manual methods often requires skilled personnel who are well-trained in the intricacies of the process.
Additionally, the variability in outcomes associated with manual preparation may necessitate re-treatments, which can add to the overall cost.
For practices or clinics with limited budgets and lower patient volumes, manual preparation may be a viable option.
However, it’s crucial to weigh the initial savings against the potential drawbacks, such as increased labor costs and the risk of inconsistent results.
Careful consideration of the specific needs and long-term goals of the practice is essential when deciding between PRP machines and manual preparation methods.
Conclusion
In the debate between PRP machines and manual preparation techniques, the choice ultimately depends on the specific needs of the practice or clinic.
PRP machines, exemplified by the SELPHYL® system, offer precision, efficiency, and reduced contamination risk.
However, they come with a substantial initial investment. Manual preparation, while cost-effective upfront, may lead to variability in PRP quality and longer processing times.
Ultimately, the decision should be based on factors such as the volume of patients, the nature of the PRP applications, and budget considerations.
For high-demand environments, PRP machines may be the preferred choice, while manual preparation might suffice in smaller settings where customization and precision are less critical.
The key is to weigh the pros and cons carefully to determine the most suitable method for harnessing the potential of PRP in your practice.

Jean Smith is a fitness enthusiast and blogger who focuses on fitness and a healthy lifestyle. She is passionate about assisting people in living healthier lifestyles and is constantly on the lookout for new and creative methods to stay fit and healthy. Her articles are excellent resources for anyone interested in improving their health and fitness.
